Fibrinogen
Family Ties
The three polypeptides comprising fibrinogen are encoded by distinct but ancestrally related genes. The domains in fibrinogen are related to domains found in FreP-A and FreP-B from sea cucumber, in scabrous proteins (regulation of neurogenesis) from Drosophila, and in ficolin proteins (lectin activity). Fibrinogen domains originated early in development, and their ability to form intermolecular interactions may be harnessed by different proteins involved in various aspects of cellular function and developmental biology.
What InterPro Tells Us
P02679 Human Fibrinogen gamma chain
InterPro Domain Architecture
![]()
InterPro Entry |
Signatures |
Graphical Match |
Method Name |
|
IPR002181 |
PF00147 |
|
Fibrinogen_C |
|
IPR002181 |
PS00514 |
|
Fibrin_AG_C_Dom |
|
IPR002181 |
SM00186 |
|
FBG |
|
IPR012290 |
G3DSA:1.20.5.50 |
|
Fibrinogen_G_N |
|
Structural Features |
|
|
|
|
1n86 |
1n86C |
|
|
|
1n86 |
1n86F |
|
|
|
1.20.5.50.9 |
1fzcC3 |
|
|
|
3.90.215.10.2 |
1fib01 |
|
|
|
4.10.530.10.1 |
1fib02 |
|
|
|
d.171.1.1 |
d1fib__ |
|
|
|
h.1.8.1 |
d1fzcc2 |
|
|
|
Structural Features |
|
|
|
|
MB_P02679 |
|
|
|
|
Splice Variant 1 |
P02679‑1 (UniProt)
|
|
|
|
IPR002181 |
PF00147 |
|
Fibrinogen_C |
|
IPR002181 |
PS00514 |
|
Fibrin_AG_C_Dom |
|
IPR002181 |
SM00186 |
|
FBG |
|
Splice Variant 2 |
P02679‑2 (UniProt) |
|
|
|
IPR002181 |
PF00147 |
|
Fibrinogen_C |
|
IPR002181 |
PS00514 |
|
Fibrin_AG_C_Dom |
|
IPR002181 |
SM00186 |
|
FBG |
From the graphical match in the top (blue) table, you can see that the signatures are all grouped into two InterPro entries for human fibrinogen gamma chain. These entries identify two domains for this protein.
DOMAIN Entries
Ø IPR002181: C-terminal globular domain from fibrinogen chains alpha/beta/gamma, represented by three signatures: PF00147 (PFAM), PS00514 (PROSITE), and SM00186 (SMART).
Ø IPR012290: Coiled coil domain from fibrinogen gamma chain, represented by one signature: G3DSA:1.20.5.50 (Gene3D).
The gamma polypeptide of fibrinogen consists of an N-terminal region that forms part of fibrinogen E domain, followed by an alpha-helical region that forms part of the fibrinogen coiled coil domain, and the C-terminal region that forms part of the fibrinogen D domain (all in conjunction with the Aa and Bb polypeptides). Both the coiled coil (IPR012290) and the C-terminal region forming the D domain (IPR002181) are represented above.
Splice variants
The two yellow tables represent known splice variants for the gamma chain, P02679-1 and P02679-2. Both of these splice variants match the signatures for the C-terminal globular domain, but fail to match the signature for the N-terminal domain. Splice variant P02679-1 comprises about 10% of the fibrinogen molecules in plasma, but is absent from those in platelets.
Structural features
The remaining eight entries in the blue table above give information on the known and predicted structure of this protein. The first seven entries present known structural data from the structural database PDB (green stripe) and the structural classification databases CATH (pink stripe) and SCOP (black stripe) (the names such as 1fzcC3 are derived from the PDB entry upon which they are based, here PDB entry 1fzc, chain C, fragment 3). The graphical match for the PDB entry 1n86 displays the full length of the original PDB entry, here covering about two-thirds of the protein. There are two PDB chains representing this protein, because there are two gamma polypeptides in a fibrinogen molecule. The CATH and SCOP entries break down the PDB data into its structural domains, and providing a structural classification for the protein domain and relating it to other structures in the PDB database.
CATH breaks the fibrinogen gamma chain into three domains:
· 1.20.5.50.9 represents an alpha-helical coiled coil (coiled coil domain)
· 3.90.215.10.2 represents an alpha helix-beta sheet complex (D domain)
· 4.10.530.10.1 represents an irregular structure (D domain)
SCOP breaks the fibrinogen gamma chain into two domains:
· h.1.8.1 represents an alpha-helical coiled coil (coiled coil domain)
·
d.171.1.1
represents an unusual fold consisting of separate alpha and beta regions (D
domain)
The remaining entry is for the structural prediction, MB_P02679, from the homology model database ModBase (yellow stripe). The homology model provides information on the predicted structure for regions of the proteins that have no known structure, here the N-terminal domain that forms part of the E domain in fibrinogen.
What the Structure Tells Us
Structures
associated with the gamma chain of human fibrinogen can be viewed using
AstexViewer®, which is linked from the Match Table via the logo ![]() on the InterPro page (please note, there is
no link directly from this page to the AstexViewer®, therefore you need to go
to the
on the InterPro page (please note, there is
no link directly from this page to the AstexViewer®, therefore you need to go
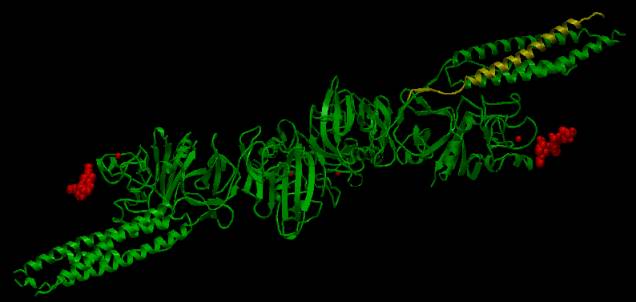
to the ![]() link on the InterPro page for P02679). The AstexViewer® displays the PDB structure with the CATH and
SCOP domains highlighted in yellow. In
the picture below, the CATH domain representing the coiled coil region from one
gamma chain is highlighted in yellow, while the ligands are highlighted in red
attached to the two D domains.
link on the InterPro page for P02679). The AstexViewer® displays the PDB structure with the CATH and
SCOP domains highlighted in yellow. In
the picture below, the CATH domain representing the coiled coil region from one
gamma chain is highlighted in yellow, while the ligands are highlighted in red
attached to the two D domains.
|
|
|
AstexView of human fibrinogen gamma chain: the coiled coil region is highlighted in yellow. |
There are
structures available for all three fibrinogen polypeptides from different organisms in the
Protein Data Bank (PDB). A detailed
description and visualisation of the structural features of these proteins can
be found at the PDB ‘Molecule of the Month’.
The crystallographic structures of fibrinogen and fibrin proteins have
provided insight into the assembly of blood clots.
Next: Table of Fibrinogen Proteins
Previous: Fibrin and
Cancer