Protein of the Month |
February 2006
MORE ON THIS MONTH’S PROTEIN
|
|
OTHER PROTEINS OF INTEREST |
|
Molecule of the Month: Amylase |
|
|
a-Amylase
By Jennifer McDowall
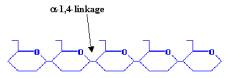
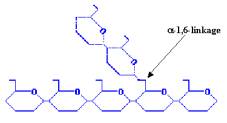
Carbohydrates usually form the bulk of the human diet, their breakdown products providing much of the energy required to sustain life. Carbohydrates consist of simple sugars (monosaccharides and disaccharides), as well as more complex compounds composed of multiple sugar units (polysaccharides), such as starch and cellulose. The largest source of starch in our diets comes from corn (maize), as well as from wheat, potatoes and rice. The starch we eat is generally a mixture of amylose, which is composed of a-1,4-linked glucose polymers (link between C1 and C4 atoms), and amylopectin, which is composed of a-1,4-linked glucose polymers branched by a-1,6-linkages.
|
|
|
|
AMYLOSE |
|
AMYLOPECTIN |
To provide energy, these complex carbohydrates first need to be broken down into their sugar components, which ultimately enter the tricarboxylic acid cycle to yield ATP and carbon dioxide using water and oxygen. Digestion of starch begins in the mouth, where salivary a‑amylase provides partial digestion, breaking down the polysaccharides into shorter oligomers. Once these reach the stomach, they are digested further by pancreatic a‑amylase, which produces even smaller oligosaccharides that can be broken down by various a‑glucosidases to monosaccharides such as glucose that are readily absorbed into the bloodstream.
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Various enzymes are involved in the breaking down and synthesis of glucosidic linkages in starch, which can be grouped into four general classes:
Breakdown
of starch:
· Hydrolysis of a-1,4-glucosidic linkages, e.g. a-amylase
· Hydrolysis of a-1,6-glucosidic linkages, e.g. pullulanase
Synthesis
of starch:
· Transglycosylation to form a-1,4-glucosidic linkages: cyclodextrin glucanotransferase
· Transglycosylation to form a-1,6-glucosidic linkages: branching enzyme
a-Amylases
In animals, a-amylases act to hydrolyse the a-1,4-glucosidic linkages in starch, glycogen (animal storage form of glucose), and dextrin (smaller than starch), but they are widely distributed in microorganisms, plants and animal secretions. a‑Amylases are synthesized as part of a multi-gene family, which is regulated to provide different isozymes in different tissues. There are two main isoforms in humans, salivary a‑amylases and pancreatic a‑amylases, which exhibit different cleavage patterns through amino acid substitutions, some near their active site regions.
Despite these differences, a‑amylases show considerable structural similarity to one another. In general, a‑amylases consists of three domains, which in human pancreatic a‑amylase have been well characterised:
Signal sequence
· Residues 1-15
Domain A
· Residues 16-114 and 184-419
· Contains active site residues (Asp212 [nucleophile], Glu248 [proton donor], Asp315).
· Contains chloride ion binding site (Arg210, Asn313, Arg352).
· N-terminal Glu residue undergoes post-translational modification thought to protect the molecule against other digestive enzymes.
Domain B
· Residues 115-183.
· Contains Ca++ binding site (Asn 115, Arg173, Asp182, His216).
Domain
C
·
Residues
420-511
· Position can vary between amylase enzymes.
Domains A and B are often considered together, as domain B occurs as an extended loop inserted within domain A. a-Amylases have at least one conserved Ca++ binding site, and most have more than one, as calcium binding is essential for maintaining the structural stability of the enzyme. The chloride ions function to activate the enzyme, which acts by a two-step mechanism involving an acid/base catalyst (Asp212) and a nucleophile (Glu248) that are responsible for the formation of the b-linked glycosyl-enzyme intermediate.
Next: a-Amylase
Inhibitors