The Sweetest Thing
focusA famous cola company launched a new product contained in a gleaming green can last year. As a regular cola drinker, I was intrigued by the packaging. After doing some research, I discovered that this variety of cola contains a sweetener called Stevia.
 Figure 1. Stevia rebaudiana. Ethel Aardvark, Wikimedia
Figure 1. Stevia rebaudiana. Ethel Aardvark, Wikimedia
Stevia is extracted from a plant, Stevia rebaudiana, found in Brazil and Paraguay. The leaves of the Stevia plant have been used for hundreds of years in both countries to sweeten local teas and medicines. The sweet taste is mainly from steviol glycoside compounds, which have up to 150 times the sweetness of sugar, but zero calories [1].
The story of Stevia gave me, a protein database curator, the idea to search for the sweetest proteins to date. I found one such protein, thaumatin (IPR001938), produced by Thaumatococcus daniellii (also known as Katemfe), a shrub from West Africa. Thaumatin is around 2,000 times sweeter than sugar [2]!
Similar to Stevia, Katemfe plants have been used by the locals for a long time; they use its leaves for wrapping food and its fruits for sweetening breads, palm wine and sour food. Their sweet proteins, thaumatin I and thaumatin II, were first identified in the 1970s in the search for non-toxic, non-calorific ‘natural’ sweeteners to replace synthetic ones [3].
 Figure 2. Katemfe plant ~from Engler et al. Marantaceae, vol. 48: [Heft 11], p. 40, fig. 8 (1902).
Figure 2. Katemfe plant ~from Engler et al. Marantaceae, vol. 48: [Heft 11], p. 40, fig. 8 (1902).
Why do plants like Katemfe produce extremely sweet proteins? The answer may lie in the plant defence systems. Under environmental stresses or pathogen attack, plants can produce proteins that help them stay alive. In the case of Katemfe, attack by a viroid (a sub-viral pathogen) induces thaumatin production. Thaumatin has also been shown to have antifungal activities, which suggests it may be part of a defence mechanism that prevents further pathogen attacks [4].
In fact, thaumatin shares a conserved site (IPR017949) with a group of pathogenesis-related proteins, also known as thaumatin-like proteins (TLPs) [5], including tobacco salt-induced protein osmotin [6] and maize antifungal protein zeamatin [7]. Like thaumatin, this group of proteins plays an essential part in plant defence against either environment stress or pathogen attack [8].
Another question is, why does thaumatin taste sweet to us? This is down to the sweetness receptors in our taste buds on our tongues. The sweet molecules (chemicals or proteins) are perceived by G-protein-coupled receptors, consisting of two subunits, T1R2 and T1R3. Certain amino acid residues in these subunits affect their ability to recognise the sweet molecules [9]. Interestingly, apes and Old World monkeys can perceive thaumatin as a sweet protein, while New World monkeys and rodents cannot [2]. In other words, the sweet taste of thaumatin for us humans could be just an evolutionary coincidence.
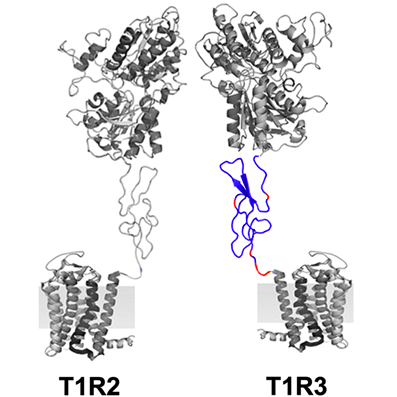 Figure 3. Sweet receptor, the peptide region involved in the response for thaumatin is shown in red [2].
Figure 3. Sweet receptor, the peptide region involved in the response for thaumatin is shown in red [2].
So far, several chemical sweeteners have been commercialised, such as aspartame, sucralose and saccharin, and many more products may yet emerge. We all know that our sugar consumption causes health problems like obesity, diabetes and tooth decay. To avoid such health issues, scientists have searched far and wide to find alternatives. Natural sweeteners, such as Stevia and thaumatin, have provided new options for us. However, with so many different products on the market, as a consumer, I am still sitting on the fence to see which ones provide the best health benefits.
 Figure 4. What should be in yours?
Figure 4. What should be in yours?
Additional information:
I. Katemfe: Katemfe is a 3-4 metre tall shrub from the rain forests of West Africa. It bears light purple flowers and a soft fruit containing shiny black seeds. The fruit is covered in a fleshy red aril, the part that contains thaumatin.
II. E numbers: Thaumatin has been approved by the European as a sweetener, known as E957. It is usually used in processed foods and has a slight licorice aftertaste.
III. Calories: Despite thaumatin containing 4 calories/gram (3.87 calories/gram for sucrose), the amount needed to be used in food or drink is extremely small, due to its high potency.
IV. Other sweet proteins: Besides thaumatin, there are a few other sweet proteins such as monellin (IPR015283), pentadin, mabinlin and brazzein [10,11].
V. Further reading: How did stevia get mainstream? -By Tom Heyden http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/magazine-22758059
Are sweeteners really bad for us? -By Claudia Hammond http://www.bbc.com/future/story/20150127-are-sweeteners-really-bad-for-us
References:
-
Cardello HM, Da Silva MA, Damasio MH., Measurement of the relative sweetness of stevia extract, aspartame and cyclamate/saccharin blend as compared to sucrose at different concentrations. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 54(2):119-30., 1999. [PMID:10646559]
-
Masuda T, Taguchi W, Sano A, Ohta K, Kitabatake N, Tani F., Five amino acid residues in cysteine-rich domain of human T1R3 were involved in the response for sweet-tasting protein, thaumatin. Biochimie. 95(7):1502-5., 2013. [PMID:23370115]
-
van der Wel H, Loeve K., Isolation and characterization of thaumatin I and II, the sweet-tasting proteins from Thaumatococcus daniellii Benth. Eur J Biochem. 31(2):221-5., 1972. [PMID:4647176]
-
Rodrigo I, Vera P, Frank R, Conejero V., Identification of the viroid-induced tomato pathogenesis-related (PR) protein P23 as the thaumatin-like tomato protein NP24 associated with osmotic stress. Plant Mol Biol. 16(5):931-4., 1991. [PMID:1859873]
-
Liu JJ, Sturrock R, Ekramoddoullah AK., The superfamily of thaumatin-like proteins: its origin, evolution, and expression towards biological function. Plant Cell Rep. 29(5):419-36., 2010. [PMID:20204373]
-
Subramanyam K, Arun M, Mariashibu TS, Theboral J, Rajesh M, Singh NK, Manickavasagam M, Ganapathi A., Overexpression of tobacco osmotin (Tbosm) in soybean conferred resistance to salinity stress and fungal infections. Planta. 236(6):1909-25., 2012. [PMID:22936305]
-
Schimoler-O’Rourke R, Richardson M, Selitrennikoff CP., Zeamatin inhibits trypsin and alpha-amylase activities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 67(5):2365-6., 2001. [PMID:11319124]
-
Monteiro S, Barakat M, Piçarra-Pereira MA, Teixeira AR, Ferreira RB. Osmotin and thaumatin from grape: a putative general defense mechanism against pathogenic fungi. Phytopathology. 93(12):1505-12, 2003. [PMID:18943614]
-
Masuda T, Mikami B, Tani F., Atomic structure of recombinant thaumatin II reveals flexible conformations in two residues critical for sweetness and three consecutive glycine residues. Biochimie. 106:33-8, 2014. [PMID:25066915]
-
Faus I, Recent developments in the characterization and biotechnological production of sweet-tasting proteins. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 53(2):145-51., 2000. [PMID:10709975]
-
Masuda T, Kitabatake N. Developments in biotechnological production of sweet proteins. 102(5):375-89. J Biosci Bioeng. 2006. [PMID:17189164]